Publication
Interferon-γ exposure of human iPSC-derived neurons alters major histocompatibility complex I and synapsin protein expression
Human epidemiological data links maternal immune activation (MIA) during gestation with increased risk for psychiatric disorders with a putative neurodevelopmental origin, including schizophrenia and autism.
Read more
Human epidemiological data links maternal immune activation (MIA) during gestation with increased risk for psychiatric disorders with a putative neurodevelopmental origin, including schizophrenia and autism.
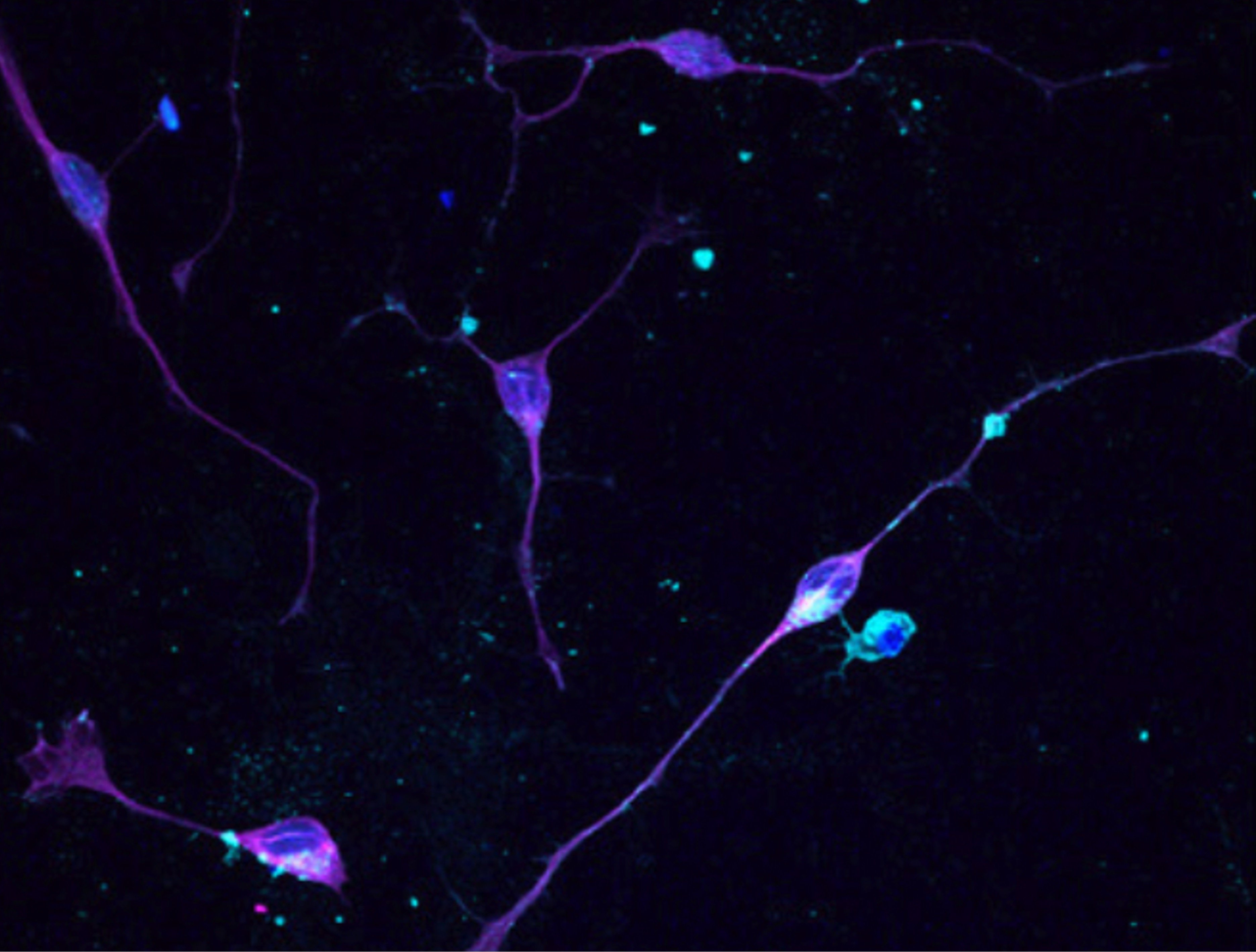
Animal models of MIA provide evidence for this association and suggest that inflammatory cytokines represent one critical link between maternal infection and any potential impact on offspring brain and behavior development. However, to what extent specific cytokines are necessary and sufficient for these effects remains unclear. It is also unclear how specific cytokines may impact the development of specific cell types. Using a human cellular model, we recently demonstrated that acute exposure to interferon-γ (IFNγ) recapitulates molecular and cellular phenotypes associated with neurodevelopmental disorders. Here, we extend this work to test whether IFNγ can impact the development of immature glutamatergic neurons using an induced neuronal cellular system. We find that acute exposure to IFNγ activates a signal transducer and activator of transcription 1 (STAT1)-pathway in immature neurons, and results in significantly increased major histocompatibility complex I (MHCI) expression at the mRNA and protein level. Furthermore, acute IFNγ exposure decreased synapsin I/II protein in neurons but did not affect the expression of synaptic genes. Interestingly, complement component 4A (C4A) gene expression was significantly increased following acute IFNγ exposure. This study builds on our previous work by showing that IFNγ-mediated disruption of relevant synaptic proteins can occur at early stages of neuronal development, potentially contributing to neurodevelopmental disorder phenotypes.
Read more