Consistent, defined and scalable human iPSC-derived disease models for Alzheimer's disease research and drug discovery
Powered by opti-ox
Powered by opti-ox
Alzheimer's disease, the most common type of dementia, is a neurodegenerative disorder that progressively undermines patients' cognitive abilities, impairing their capacity to create and retrieve memories. Studying Alzheimer’s disease remains a significant challenge, in part because of difficulties accurately emulating the disease's pathophysiology in vitro.
There is a pressing need for an in vitro model of Alzheimer's disease that can be used to accurately and reliably study the effect of disease-associated mutations, disease progression and to identify potential therapeutic targets. ioDisease Model Cells provide scientists with defined, consistent and scalable human iPSC-derived cells engineered with common monogenic Alzheimer’s disease-related mutations, helping improve the translatability of in vitro research.
Discover ioDisease Model Cells for modelling Alzheimer’s disease in vitro below.
.png)
Study functional neural networks
Modelling of cellular interactions by culturing excitatory and inhibitory neurons with astrocytes.

Model disease progression
Learn how to study the role of C5a and other proteins in driving neuroinflammation.
.png)
Analyse cytokine profiles
Investigate potential therapeutic compounds that can modulate microglial activation by measuring changes in cytokine secretion.
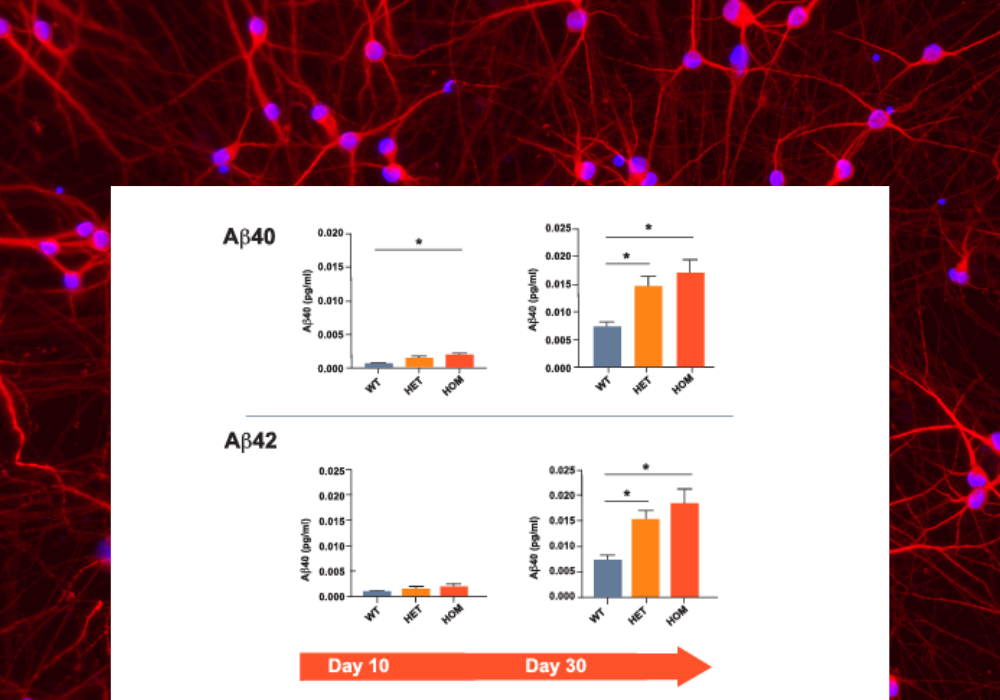
Study disease-related phenotypes
Quantification of 𝛽-amyloid peptide secretion in an Alzheimer’s disease model toolkit with a genetically matched control.

Building consistent in vitro assays for CNS drug development
Learn how ioMicroglia offered Concept Life Sciences functional cells with low inter-lot variability, ensuring consistent assay performance, facilitating large scale screening studies.
Scalable 3D models for screening
Find out how Inventia Life Science generated functional 3D neuronal models in 96- and 384-well formats that closely resembled the human brain.
.png)
Quickly identify disease risk factors
Discover how Professor Srivastava, King's College London, generated publishable data in just 12 weeks.
CRISPR-Ready ioCells offer a fast and simple toolkit for gene editing in human iPSC-derived neurons and glia. Engineered to constitutively express Cas9 nuclease or dCas9 variants, these cells enable scientists to easily knockout, activate or interfere with their gene of interest in physiologically relevant cells in a matter of days.
Access our platform to generate custom ioCells to precisely answer your drug discovery and disease research questions.
