












cat no | io1069
ioGlutamatergic Neurons PSEN1 M146L/M146L
Human iPSC-derived Alzheimer's disease model
-
Cryopreserved human iPSC-derived cells powered by opti-ox that are ready for experiments in days
-
Functional, excitatory neurons, engineered with a mutation in PSEN1 for Alzheimer's disease research
-
Disease-related phenotype demonstrated by increased ratio of A𝛽42:40 and A𝛽42:38 peptides

Human iPSC-derived Alzheimer's disease model

PSEN1 M146L disease models recapitulate an increase in amyloid beta peptide ratios observed in Alzheimer's disease patients
ioGlutamatergic Neurons PSEN1 M146L disease model cells show an increase in the ratio of A𝛽42:40 and A𝛽42:38 compared to the wild type, genetically matched control.
-
ioGlutamatergic Neurons wild type (WT) and PSEN1 M146L heterozygous (HET) clones CL8 (io1072S), CL60 and CL57, and homozygous (HOM) clones CL15 (io1069S), CL19 and CL57, were seeded at 30,000 cells/cm2 in 24-well plates and cultured for 30 days according to the user manual. Supernatant was collected at days 10, 20, and 30; data shown for day 30 only.
-
Levels of A𝛽38, A𝛽40 and A𝛽42 peptides were quantified using the V-PLEX A𝛽 Peptide Panel 1 (6E10) Kit (MSD K15200E-1). Data were obtained from two independent experiments and are shown as mean ± SEM. Data were analysed statistically using one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post-hoc analysis. * p<0.05 ***p<0.001 **** p<0.0001.
-
Expression levels for specific genes of interest in the disease model products io1072 (CL8, het) and io1069 (CL15, hom) and the additional clones (CL60, CL71, CL19, CL57) can be requested by contacting technical@bit.bio

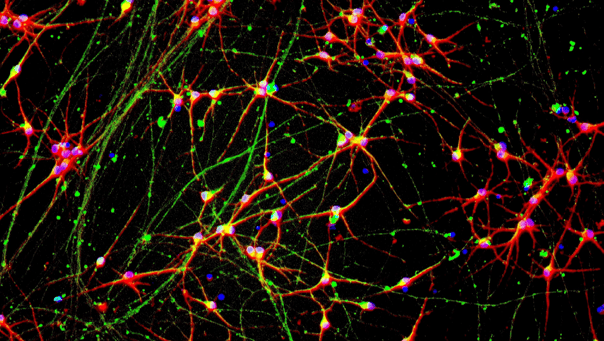
ioGlutamatergic Neurons PSEN1 M146L/M146L express neuron-specific markers comparably to the wild type control
Immunofluorescent staining on post-revival day 11 demonstrates similar homogenous expression of pan-neuronal proteins MAP2 and TUBB3 (upper panel) and glutamatergic neuron-specific transporter VGLUT2 (lower panel) in ioGlutamatergic Neurons PSEN1 M146L/M146L compared to the genetically matched control. 100X magnification.

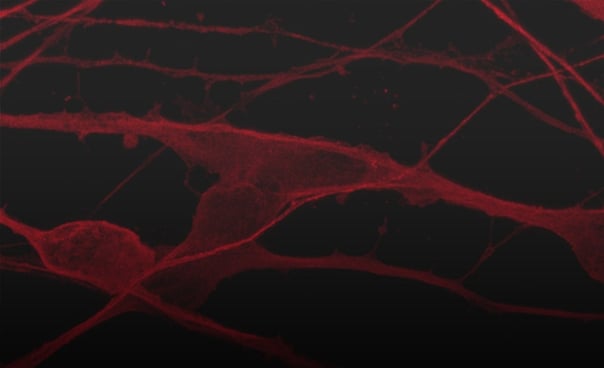
ioGlutamatergic Neurons PSEN1 M146L/M146L form structural neuronal networks by day 11
ioGlutamatergic Neurons PSEN1 M146L/M146L mature rapidly, show glutamatergic neuron morphology and form structural neuronal networks over 11 days, highly similar to the genetically matched control. Day 1 to 11 post thaw; 100X magnification.

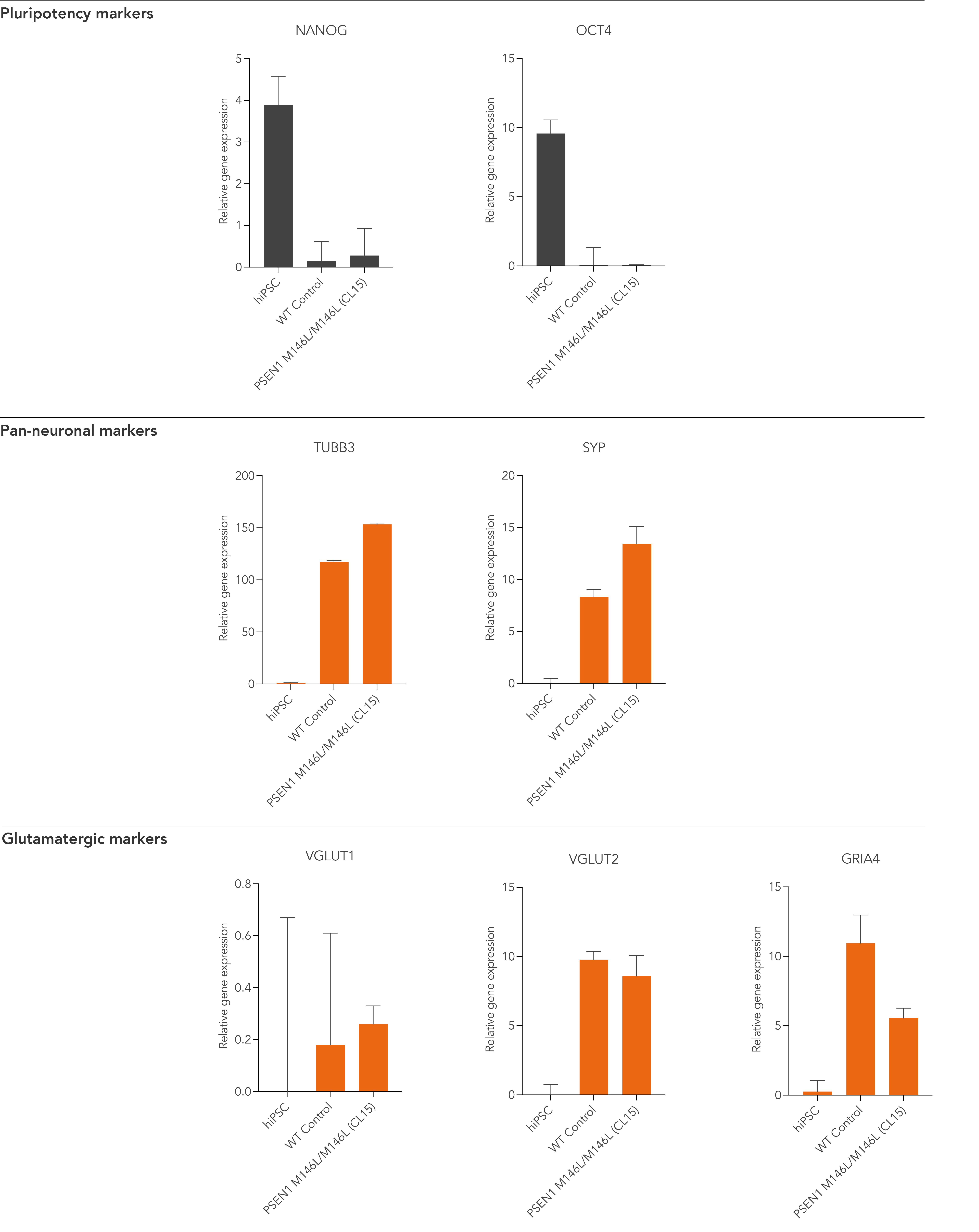
ioGlutamatergic Neurons PSEN1 M146L/M146L demonstrate gene expression of neuronal-specific and glutamatergic-specific markers following deterministic programming
Gene expression analysis demonstrates that ioGlutamatergic Neurons PSEN1 M146L/M146L and wild-type ioGlutamatergic Neurons (WT Control) lack the expression of pluripotency markers (NANOG and OCT4) at day 11, whilst robustly expressing pan-neuronal (TUBB3 and SYP) and glutamatergic-specific (VGLUT1 and VGLUT2) markers, as well as the glutamate receptor GRIA4. Gene expression levels were assessed by RT-qPCR (data normalised to HMBS; cDNA samples of the parental human iPSC line (hiPSC) were included as reference). Data represents day 11 post-revival samples, n=2 replicates.

Disease-related PSEN1 is expressed in ioGlutamatergic Neurons PSEN1 M146L/M146L following deterministic programming
RT-qPCR analysis demonstrates a similar expression level of the PSEN1 gene in both wild type ioGlutamatergic Neurons (WT Control) and ioGlutamatergic Neurons PSEN1 M146L/M146L at day 11 post-revival. Data normalised to HMBS, n=2 replicates.

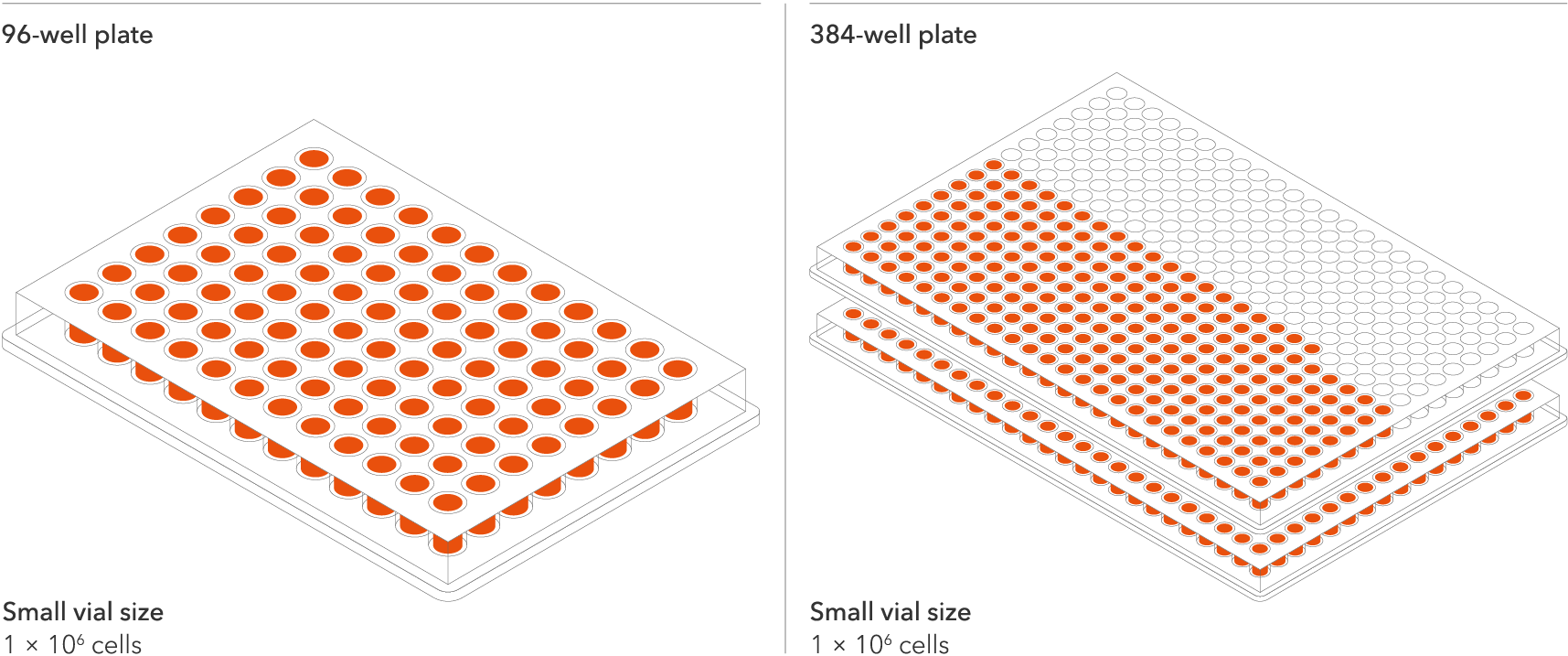
Industry leading seeding density
The recommended minimum seeding density is 30,000 cells/cm2, compared to up to 250,000 cells/cm2 for other similar products on the market. One small vial can plate a minimum of 0.7 x 24-well plate, 1 x 96-well plate, or 1.5 x 384-well plates. This means every vial goes further, enabling more experimental conditions and more repeats, resulting in more confidence in the data.
Vial limit exceeded
A maximum number of 20 vials applies. If you would like to order more than 20 vials, please contact us at orders@bit.bio.









Hoescht(blue)_day12v2.png?width=604&name=bit.bio_ioGlutamatergic%20Neurons_20xMAP2(red)Hoescht(blue)_day12v2.png)
Hoescht(blue)TUBB3(blue)_day4.jpg?width=604&name=bit.bio_ioGlutamatergic%20Neurons_60xMAP2(red)Hoescht(blue)TUBB3(blue)_day4.jpg)

.png?width=1860&height=1260&name=bit.bio_3x2_ioGlutamatergic%20Neurons_MAP2_Hoescht_x20_hi.res%20(1).png)









