cat no | io1098
CRISPRi-Ready
ioGlutamatergic Neurons
Human iPSC-derived glutamatergic neurons ready for gene repressions and CRISPRi screens
Place your order
Confidently investigate your phenotype of interest across multiple clones with our disease model clone panel. Detailed characterisation data (below) and bulk RNA sequencing data (upon request) help you select specific clones if required.
per vial
A maximum number of 20 vials applies. If you would like to order more than 20 vials, please contact us at orders@bit.bio.
For academic discounts or bulk pricing inquiries, contact us









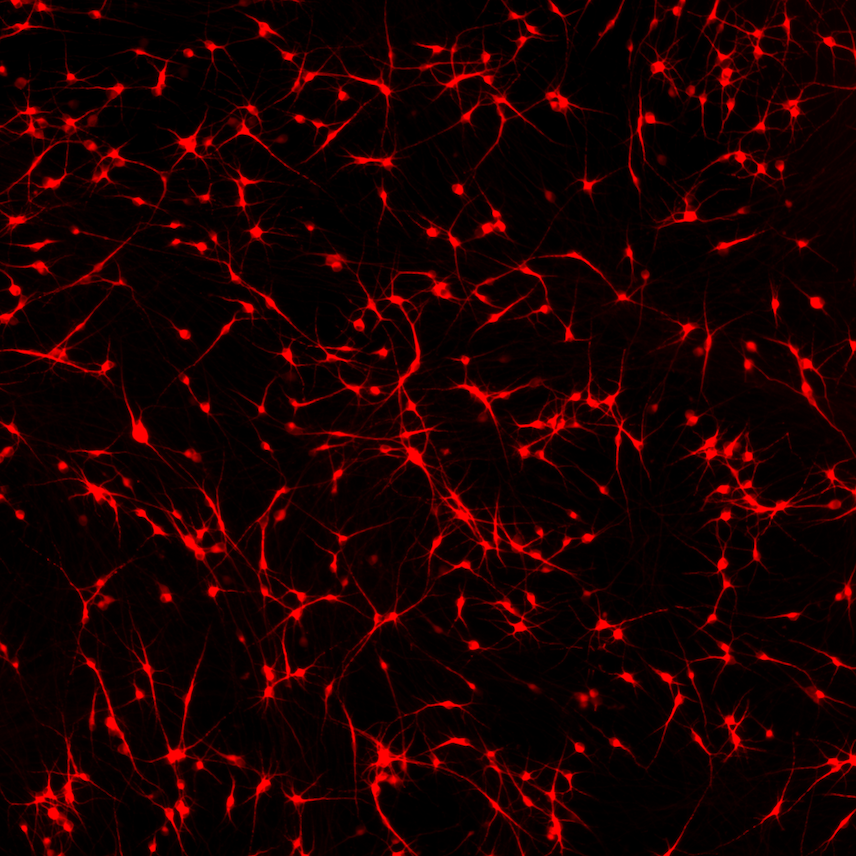
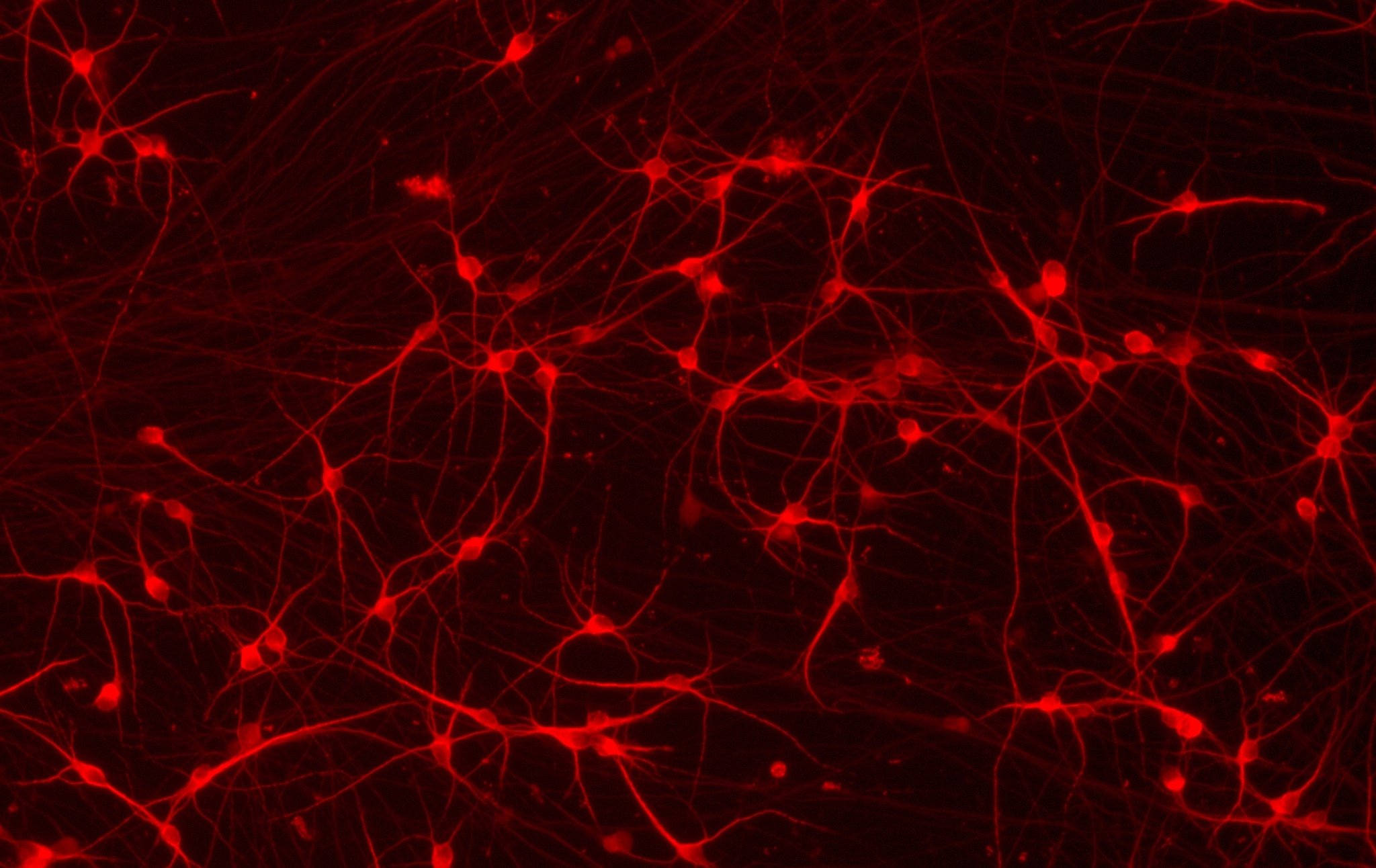
Hoescht(blue)TUBB3(blue)_day4.jpg?width=604&name=bit.bio_ioGlutamatergic%20Neurons_60xMAP2(red)Hoescht(blue)TUBB3(blue)_day4.jpg)
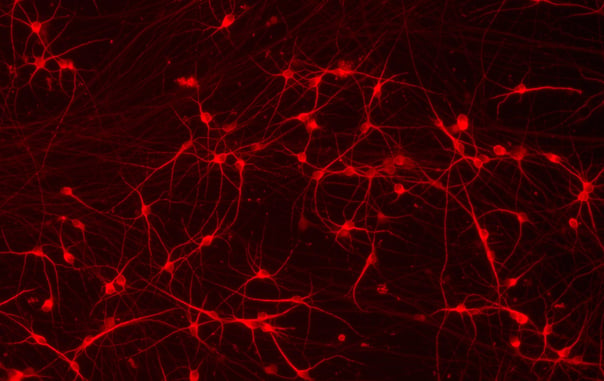
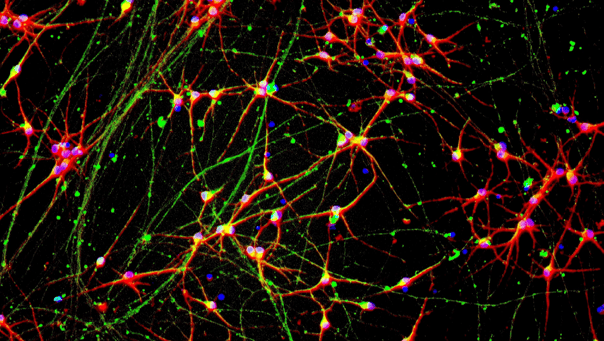
_MAP2(R)_DAPI(B)_%20comp.jpg?width=604&name=a-HTT50CAGWT_Overlay__TUBB3(G)_MAP2(R)_DAPI(B)_%20comp.jpg)
 Emmanouil Metzakopian
Emmanouil Metzakopian