cat no | io1099
CRISPRa-Ready ioGlutamatergic Neurons
Human iPSC-derived glutamatergic neurons ready for gene activations and CRISPR screens
-
Cryopreserved human iPSC-derived cells powered by opti-ox that are ready for experiments in days
-
Neurons for functional genomics, stably expressing modified Cas9 for gene activations & CRISPR screens
-
Consistent, functional excitatory neurons that form neuronal networks within days

Human iPSC-derived glutamatergic neurons ready for gene activations and CRISPR screens

Flow cytometry analysis demonstrates gene activation of CD274 upon lentiviral guide RNA delivery
Flow cytometry analysis confirms robust CD274 gene activation in CRISPRa-Ready ioGlutamatergic Neurons following lentiviral delivery of a CD274-targeting gRNA on day 3 post-thaw. Gene activation was measured by flow cytometry after five days of culture.
(A) 44% of cells received the CD274-targeting gRNA via lentiviral transduction, as indicated by GFP expression.
(B) Functionality of the dCas9-based transcriptional activator is demonstrated by a five-fold increase in CD274 protein expression (red histogram) compared to non-targeting gRNA controls (grey histogram), measured by geometric mean fluorescence intensity (GMFI) in the GFP+ population.

Activation levels depend on the chosen target and gRNA design
Flow cytometry analysis of CD55 and CD4 protein expression in CRISPRa-Ready ioGlutamatergic Neurons 5 days after delivery of gRNA. Guide RNAs were delivered on day 3 post-thaw via lentiviral transduction.
Designing gRNAs for CRISPR activation is complex and requires precise targeting of regulatory regions near the transcription start site; efficacy is significantly affected by factors such as chromatin accessibility and epigenetic modifications.
Guide RNA design tools include CHOPCHOP and CRISPick. Our team is also available to help with gRNA design, contact technical@bit.bio.

No silencing of the transcriptional activation domain
Bulk RNA sequencing analysis was performed on CRISPRa-Ready ioGlutamatergic Neurons (CRISPRa) and CRISPRi-Ready ioGlutamatergic Neurons (CRISPRi) at the iPSC stage and on days 1, 7, 14 and 21 post-revival.
Gene expression profiling revealed sustained expression of the transcriptional activation domain in CRISPRa-Ready ioGlutamatergic Neurons throughout the culture period, while no expression of the transcriptional activation domain was detected in the control line (CRISPRi-Ready ioGlutamatergic Neurons).

CRISPRa-Ready ioGlutamatergic Neurons form structural neuronal networks by day 11
CRISPRa-Ready ioGlutamatergic Neurons mature rapidly, show glutamatergic neuron morphology and form structural neuronal networks over 11 days, highly similar to wild-type ioGlutamatergic Neurons. Day 1 to 11 post-thaw; 10X magnification.

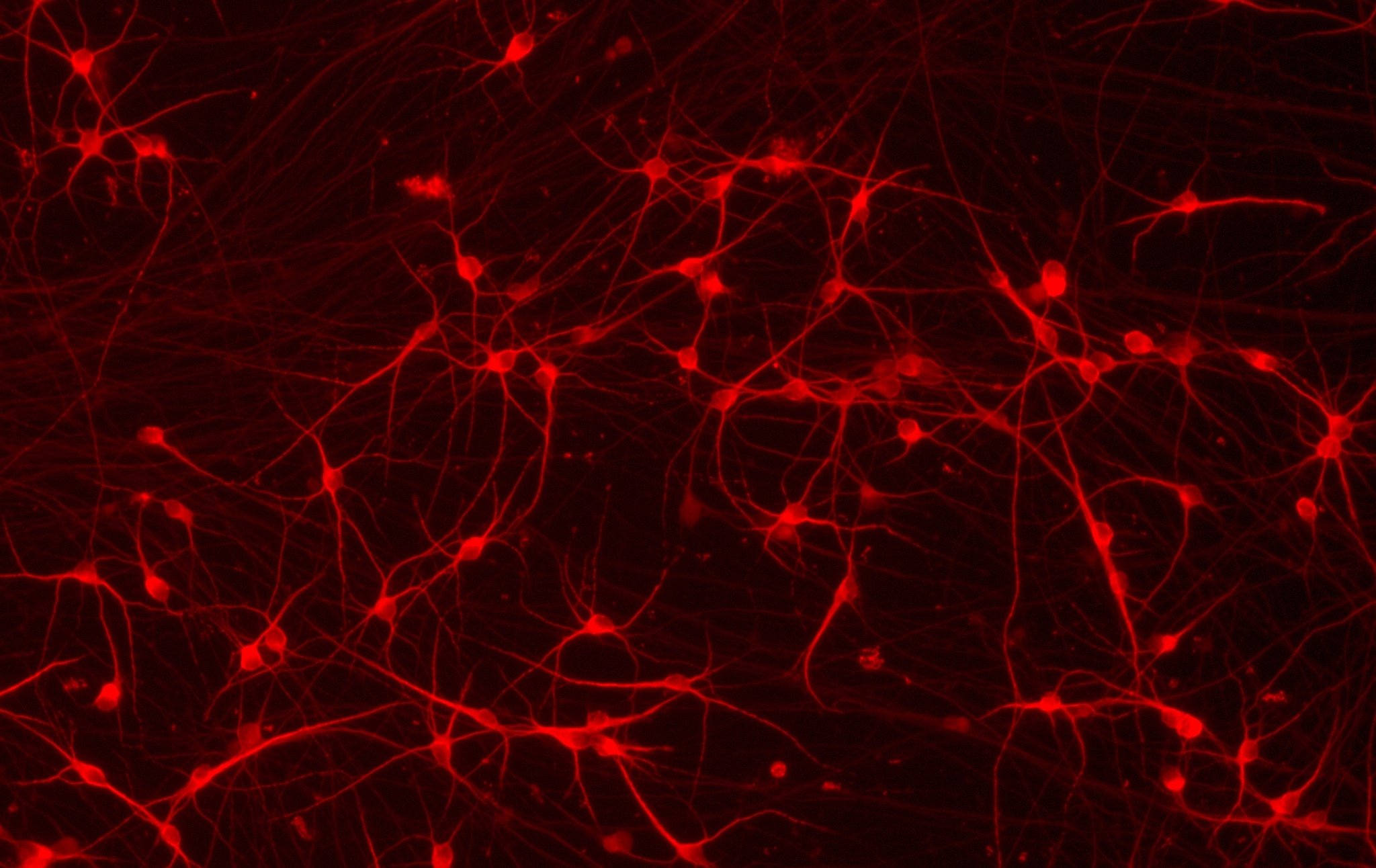
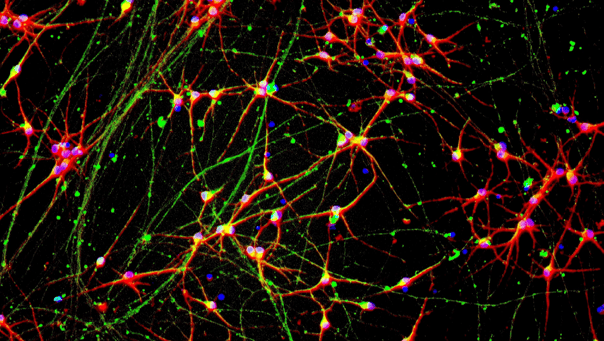
CRISPRa-Ready ioGlutamatergic Neurons express neuron-specific markers
Immunofluorescent staining on day 11 post-revival demonstrates similar homogenous expression of pan-neuronal proteins MAP2 and TUBB3 (upper panel) and glutamatergic neuron-specific transporter VGLUT2 (lower panel) in CRISPRa-Ready ioGlutamatergic Neurons compared to wild-type ioGlutamatergic Neurons. 10X magnification.

CRISPRa-Ready ioGlutamatergic Neurons demonstrate gene expression of neuronal-specific and glutamatergic-specific markers following deterministic cell programming
Gene expression analysis at day 11 demonstrates that CRISPRa-Ready ioGlutamatergic Neurons (CRISPRa) and wild-type ioGlutamatergic Neurons (WT) lack the expression of pluripotency markers (OCT4 and NANOG), while robustly expressing pan-neuronal (TUBB3 and SYP) and glutamatergic-specific (VGLUT1 and VGLUT2) markers, as well as the glutamate receptor GRIA4.
Gene expression levels were assessed by RT-qPCR. Data normalised to HMBS; cDNA samples of the parental human iPSC line (iPSC) were included as reference; n=3 replicates.

Whole transcriptome analysis demonstrates comparable transcriptomic profiles between CRISPRa-Ready ioGlutamatergic Neurons and wild-type ioGlutamatergic Neurons
Bulk RNA sequencing analysis was performed on CRISPRa-Ready ioGlutamatergic Neurons (CRISPRa) and wild-type ioGlutamatergic Neurons (WT) at the iPSC stage and on days 0 and 11 during the stabilisation to maturation phase.
Principal component analysis captured the variance in gene expression between CRISPRa and WT, revealing comparable expression profiles between samples of each product at corresponding time points. Note: data generated from cells in continuous culture.
Vial limit exceeded
A maximum number of 20 vials applies. If you would like to order more than 20 vials, please contact us at orders@bit.bio.





_MAP2(R)_DAPI(B)_%20comp.jpg?width=604&name=a-HTT50CAGWT_Overlay__TUBB3(G)_MAP2(R)_DAPI(B)_%20comp.jpg)
Hoescht(blue)TUBB3(blue)_day4.jpg?width=604&name=bit.bio_ioGlutamatergic%20Neurons_60xMAP2(red)Hoescht(blue)TUBB3(blue)_day4.jpg)
 Emmanouil Metzakopian
Emmanouil Metzakopian