cat no | io1013
ioGlutamatergic Neurons PRKN R275W/WT
Human iPSC-derived Parkinson's disease model
- Cryopreserved human iPSC-derived cells powered by opti-ox that are ready for experiments in days
- In vitro cell model engineered to carry a mutation in PRKN for Parkinson's disease research
- Consistent, functional excitatory neurons that form neuronal networks within days

Human iPSC-derived Parkinson's disease model

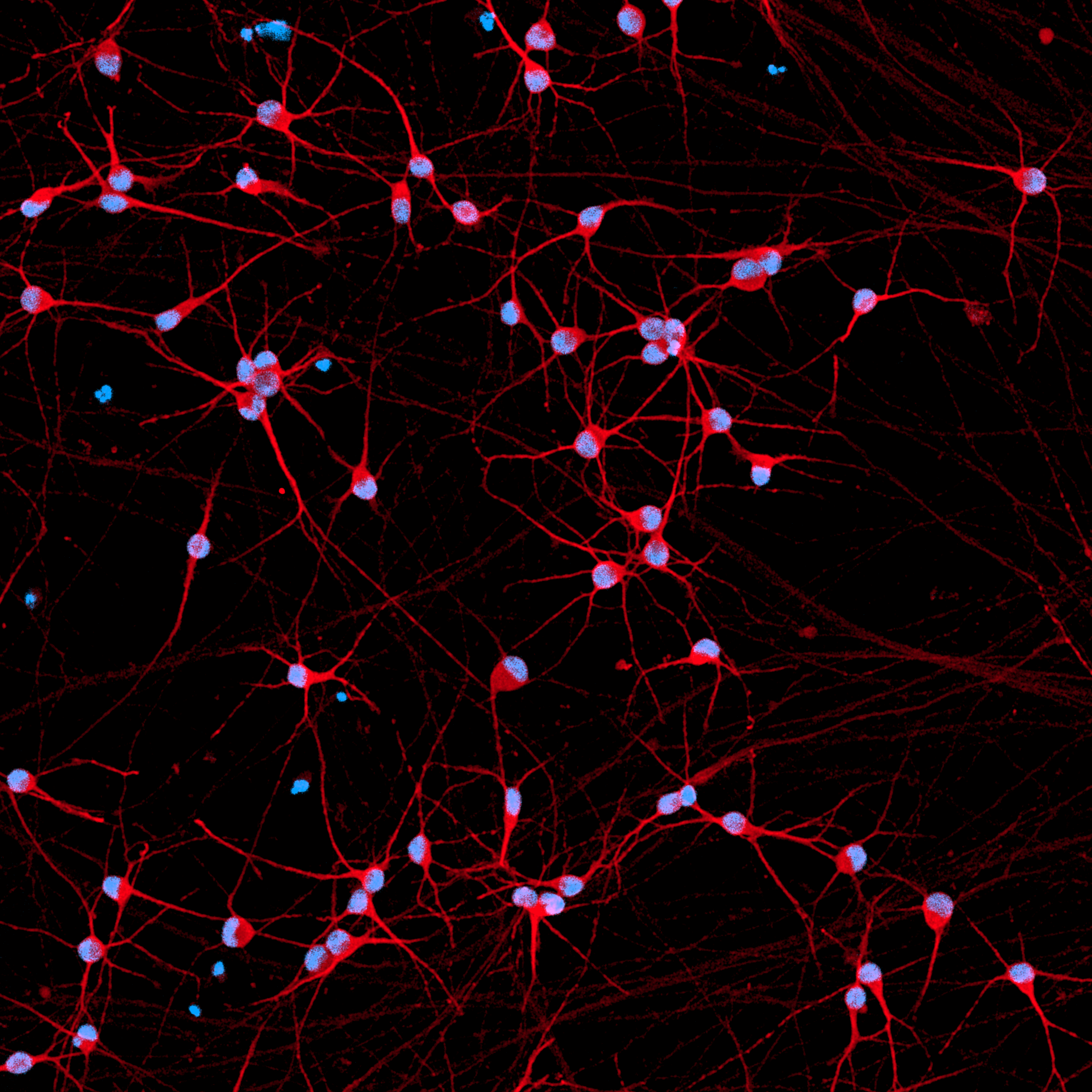
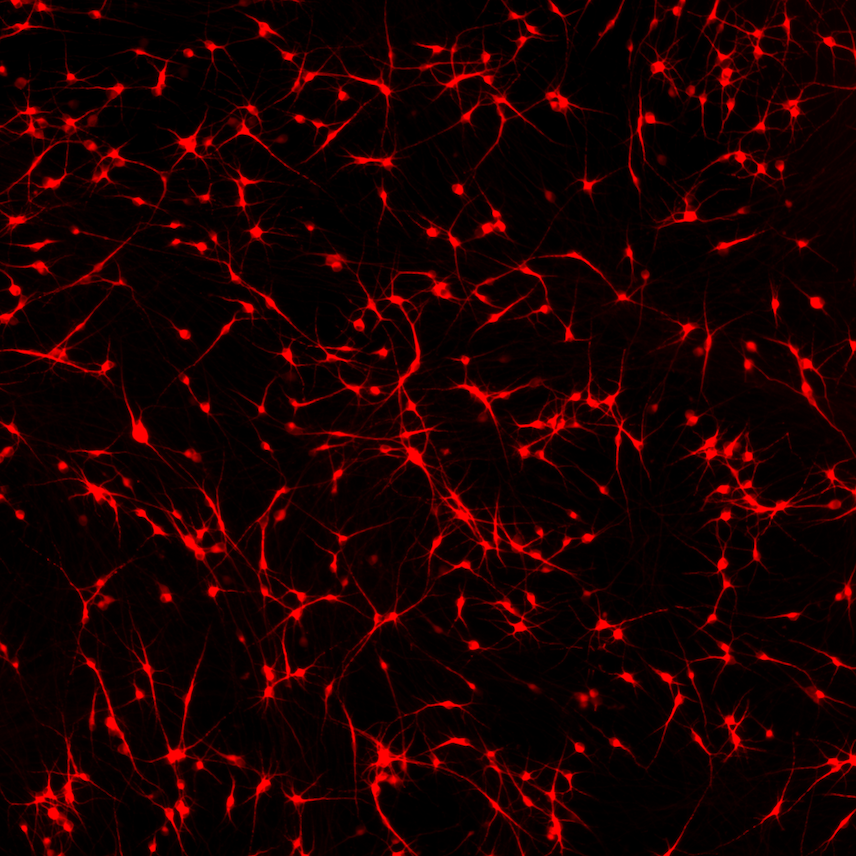
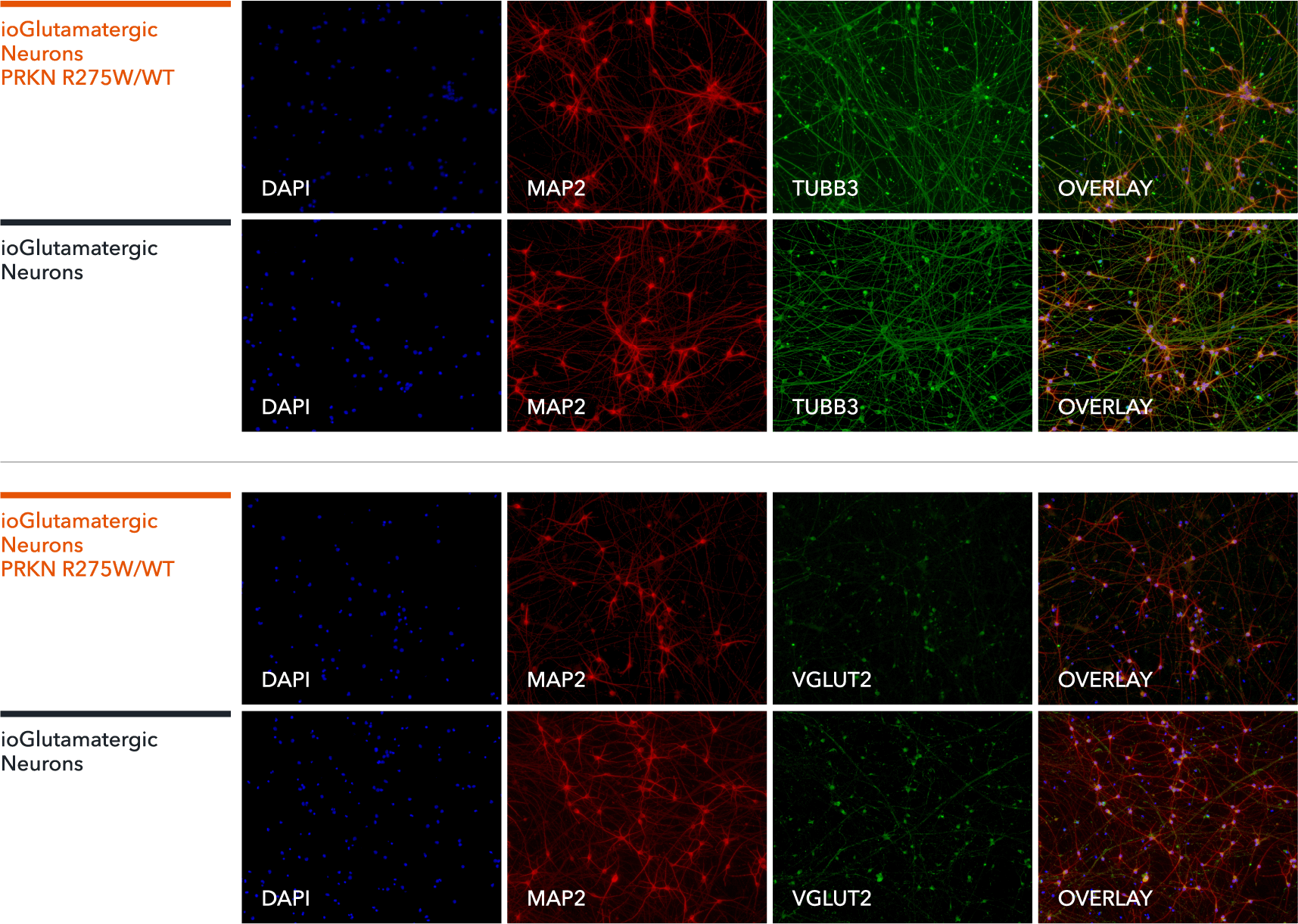
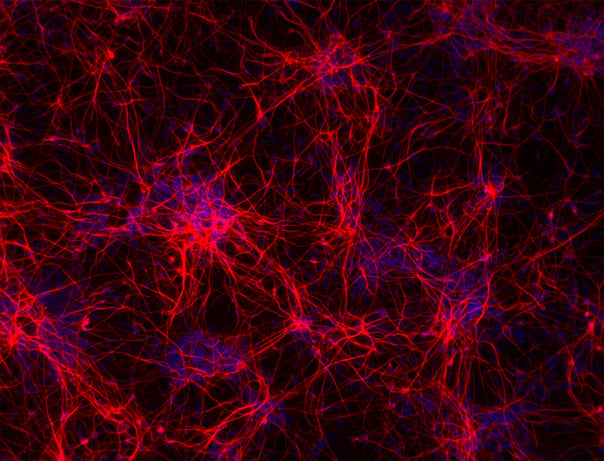
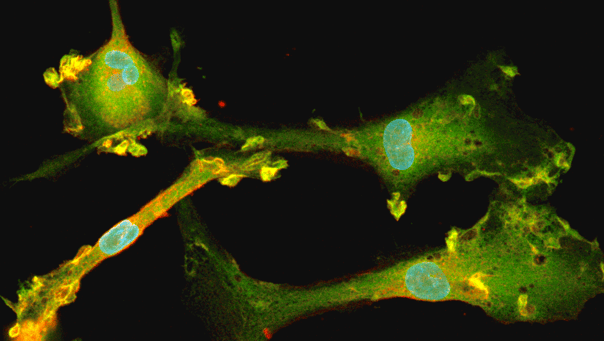
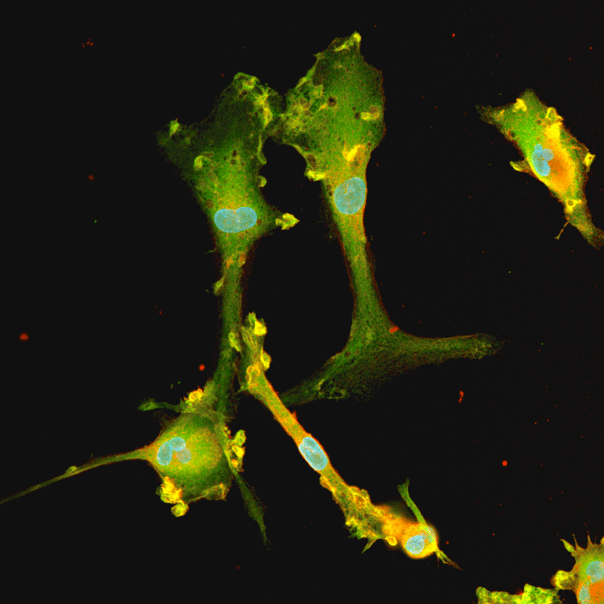
ioGlutamatergic Neurons PRKN R275W/WT express neuron-specific markers comparably to the genetically matched control
Immunofluorescent staining on post-revival day 11 demonstrates similar homogenous expression of pan-neuronal proteins TUBB3 and MAP2 (upper panel) and glutamatergic neuron-specific transporter VGLUT2 (lower panel) in ioGlutamatergic Neurons PRKN R275W/WT compared to the wild-type control. 100X magnification.

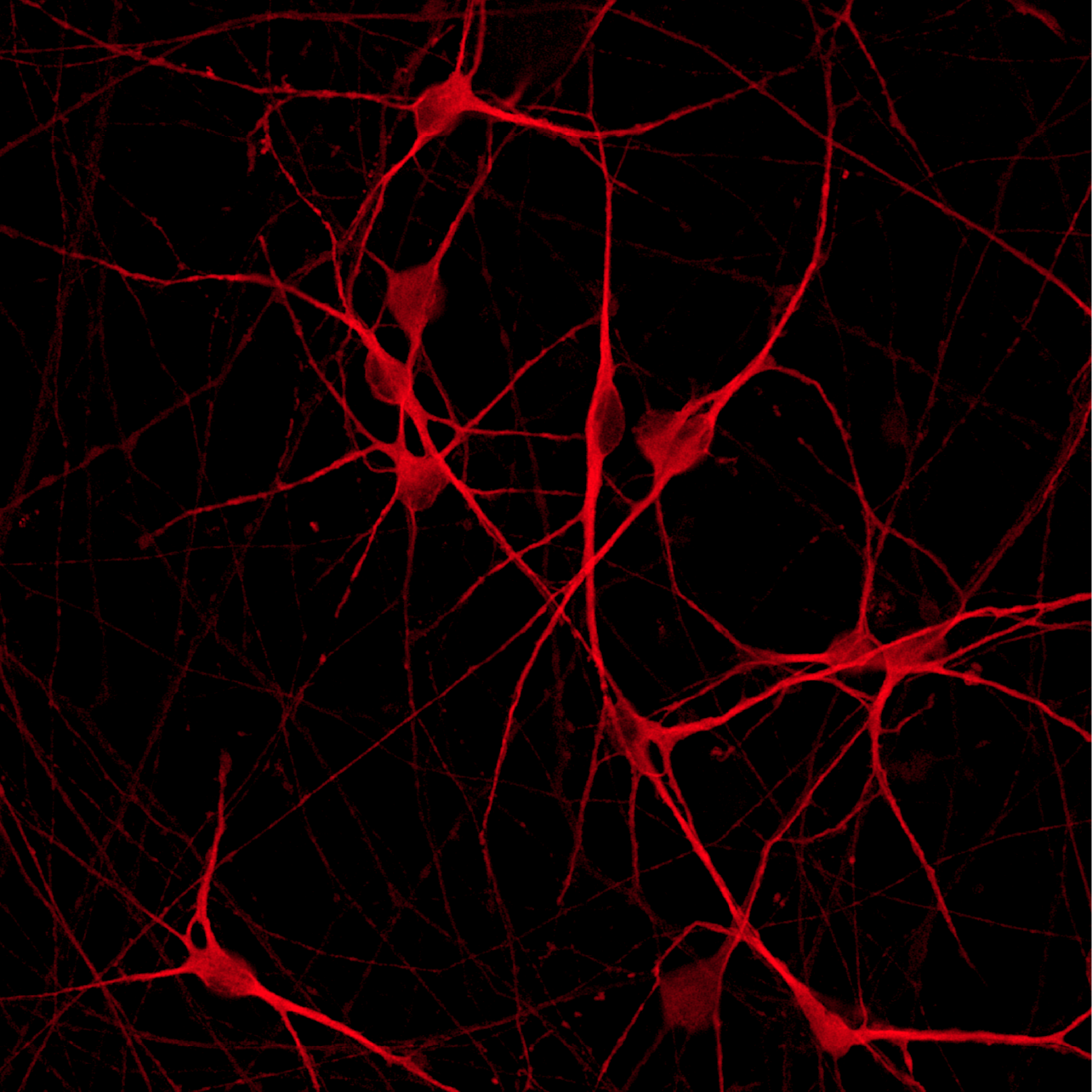
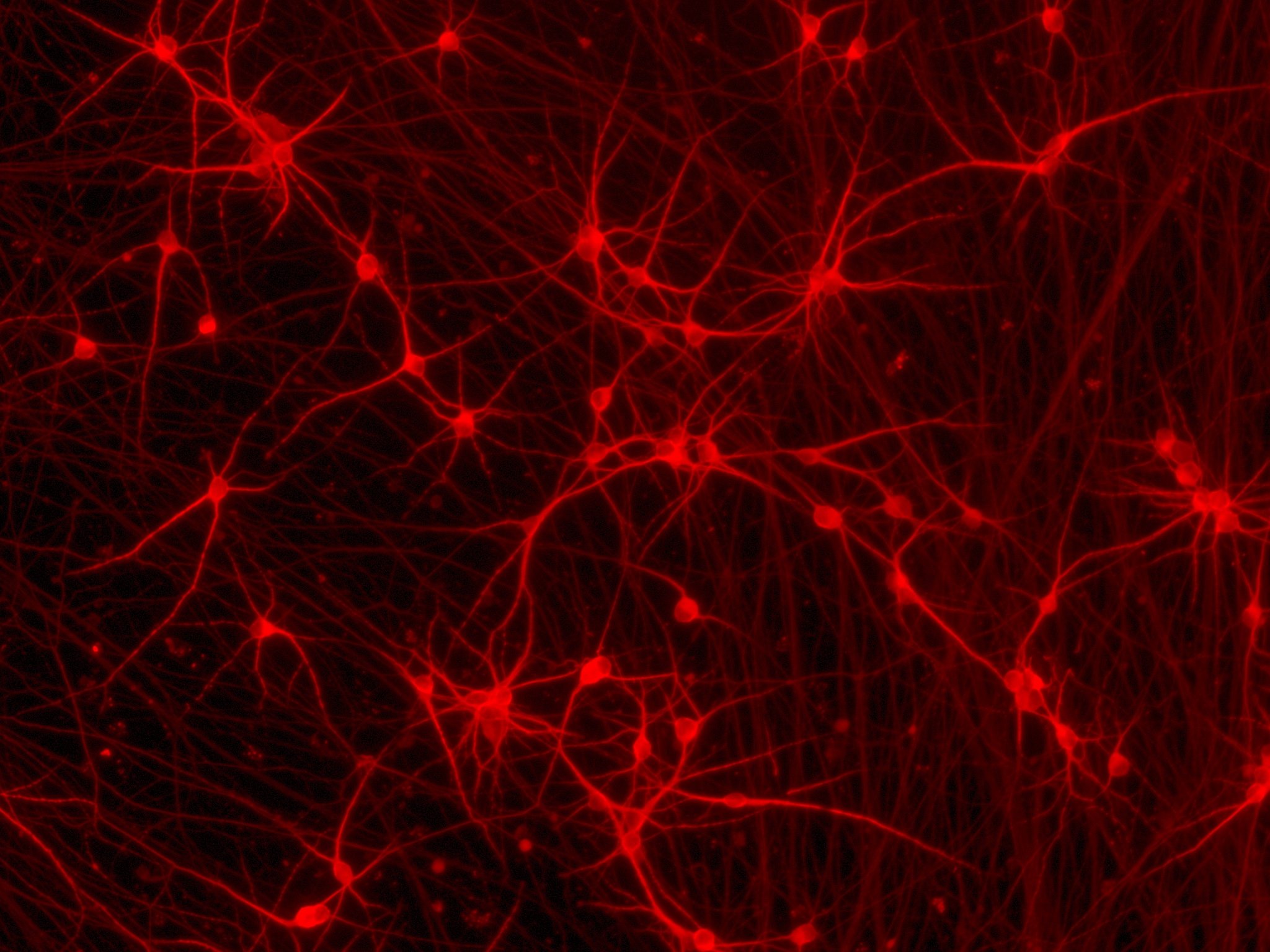
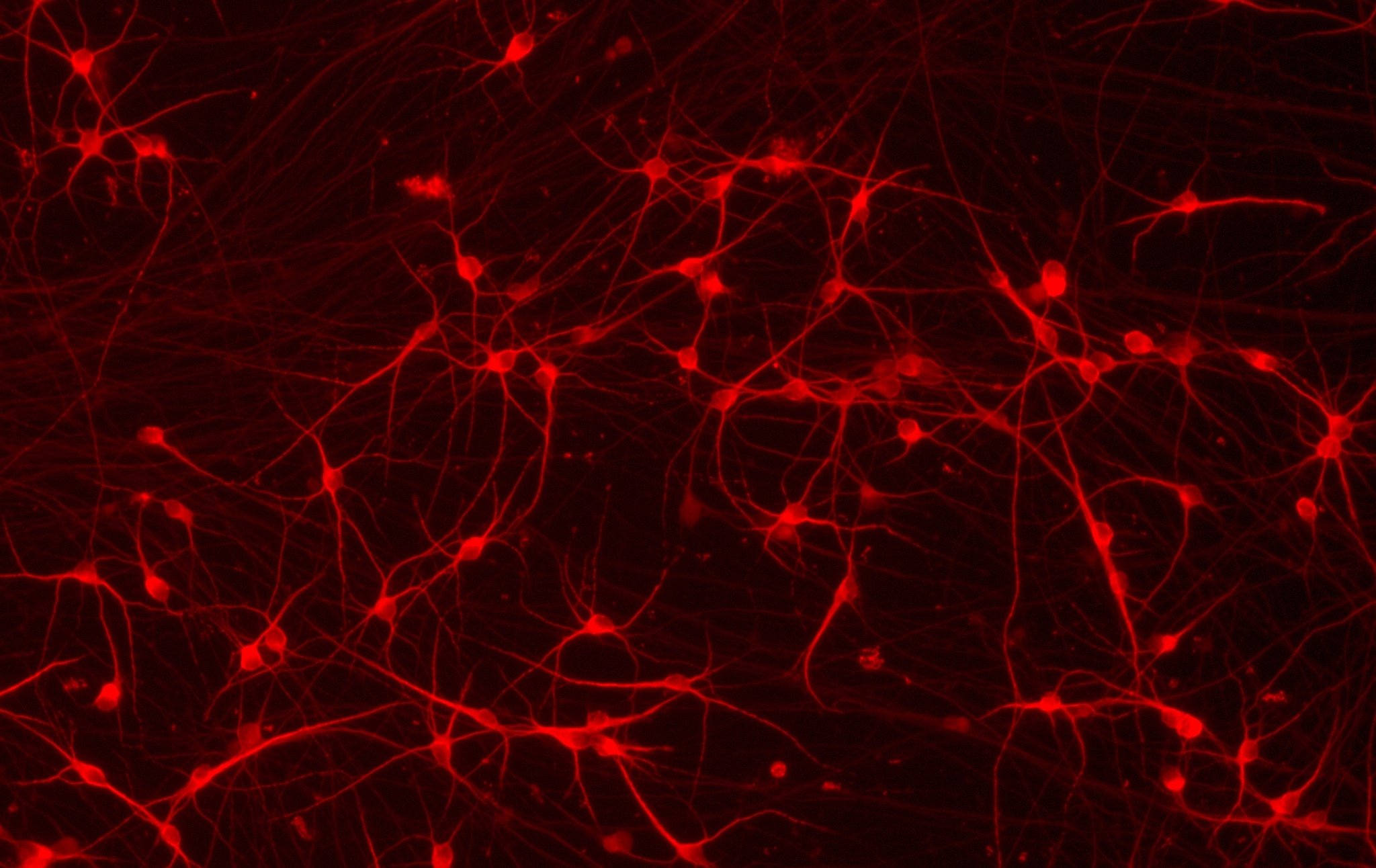
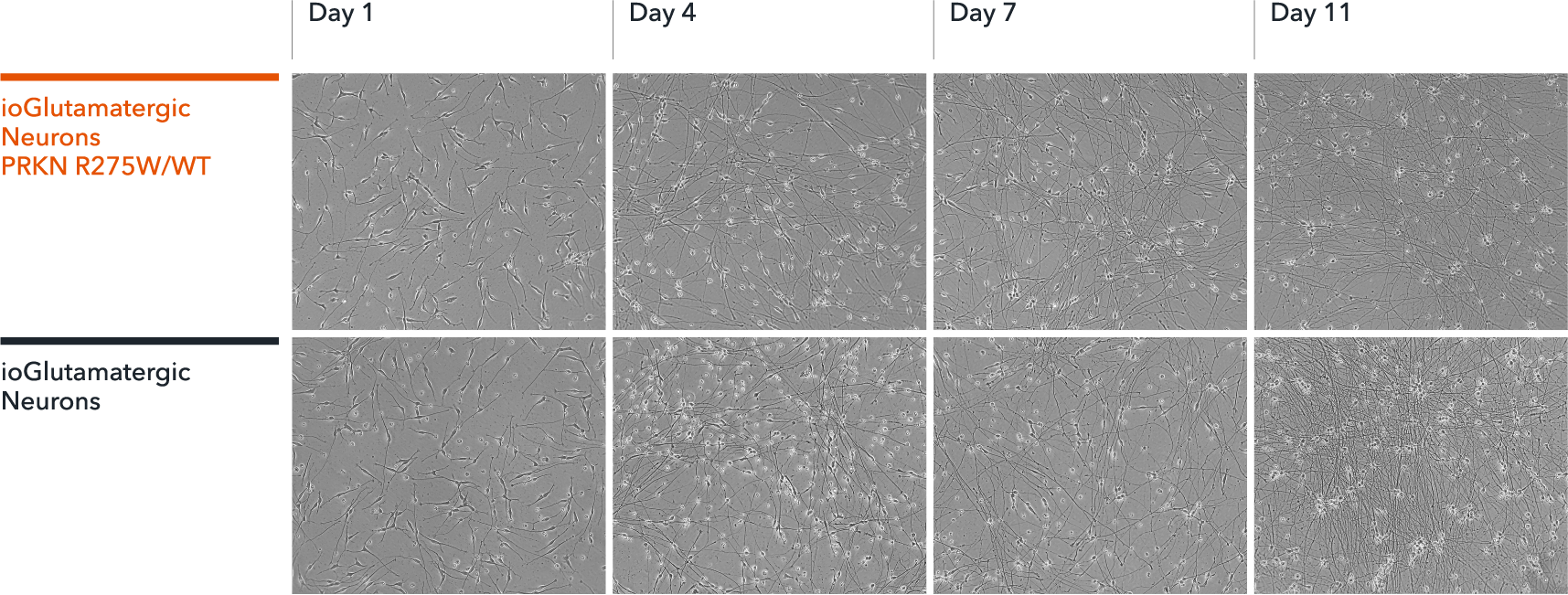
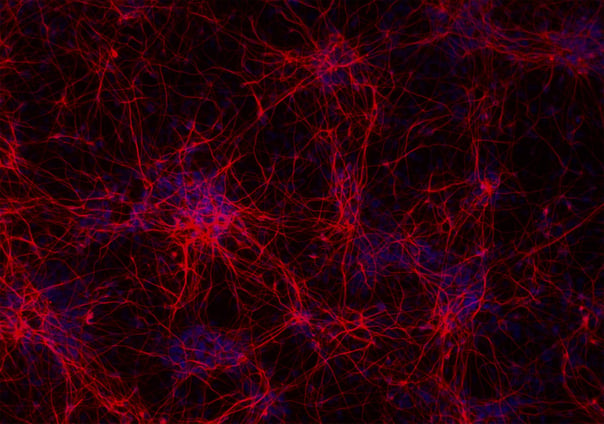
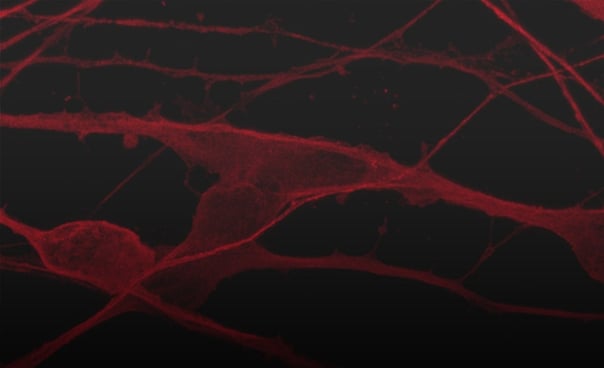
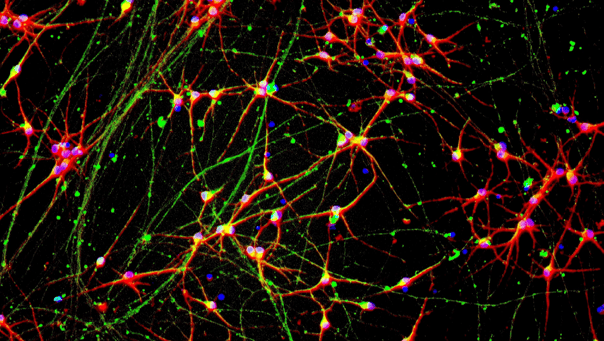
ioGlutamatergic Neurons PRKN R275W/WT form structural neuronal networks by day 11
ioGlutamatergic Neurons PRKN R275W/WT mature rapidly, show glutamatergic neuron morphology and form structural neuronal networks over 11 days, when compared to the wild-type control. Day 1 to 11 post thawing; 100X magnification.

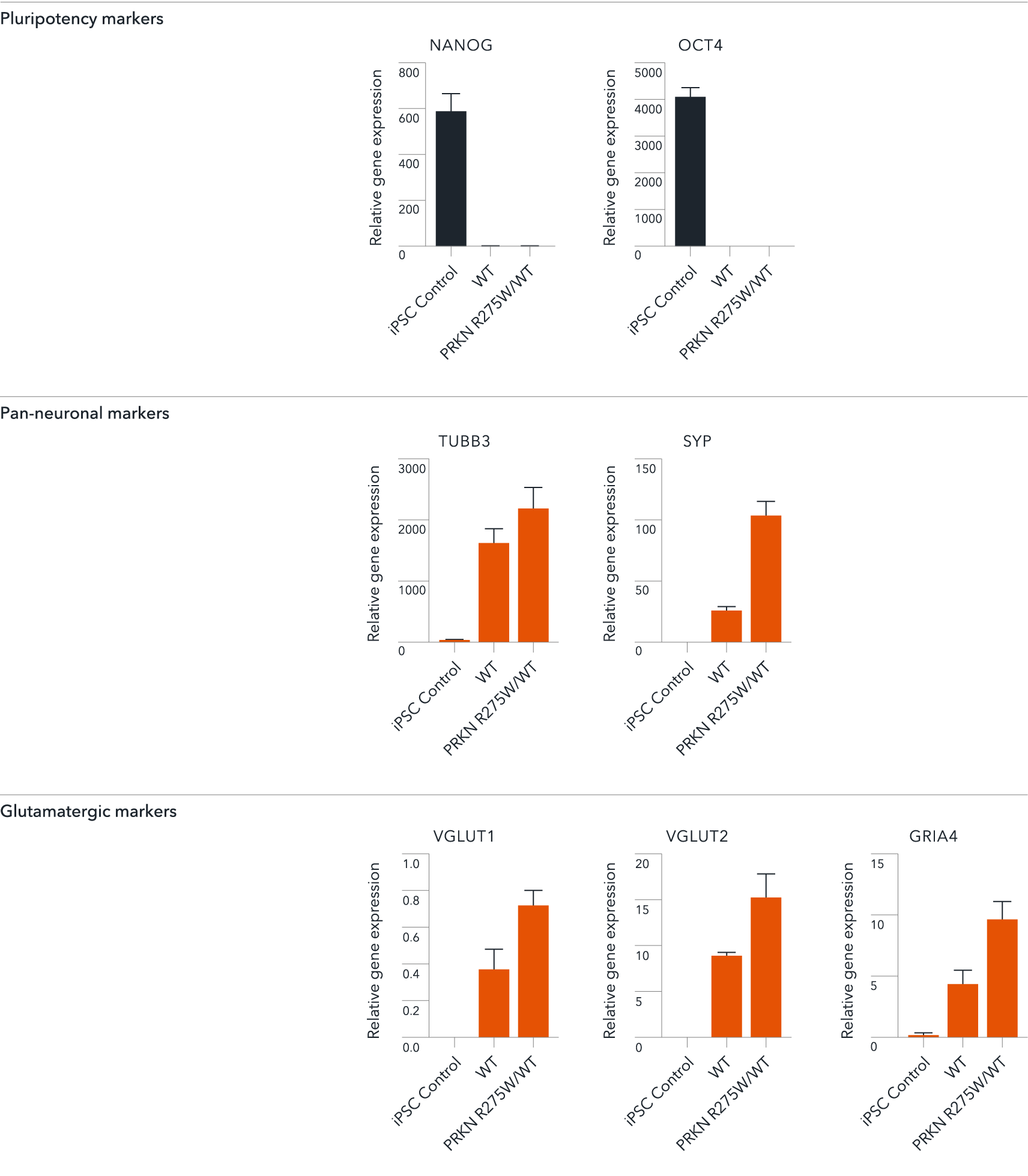
ioGlutamatergic Neurons PRKN R275W/WT demonstrate gene expression of neuronal and glutamatergic-specific markers following deterministic programming
Gene expression analysis demonstrates that ioGlutamatergic Neurons PRKN R275W/WT and the wild-type control (WT) lack the expression of pluripotency markers (NANOG and OCT4) at day 11, whilst robustly expressing pan-neuronal (TUBB3 and SYP) and glutamatergic specific (VGLUT1 and VGLUT2) markers, as well as the glutamate receptor GRIA4. Gene expression levels were assessed by RT-qPCR (data normalised to HMBS; cDNA samples of the parental human iPSC line (hiPSC) were included as reference). Data represents day 11 post-revival samples, n=2 replicates.

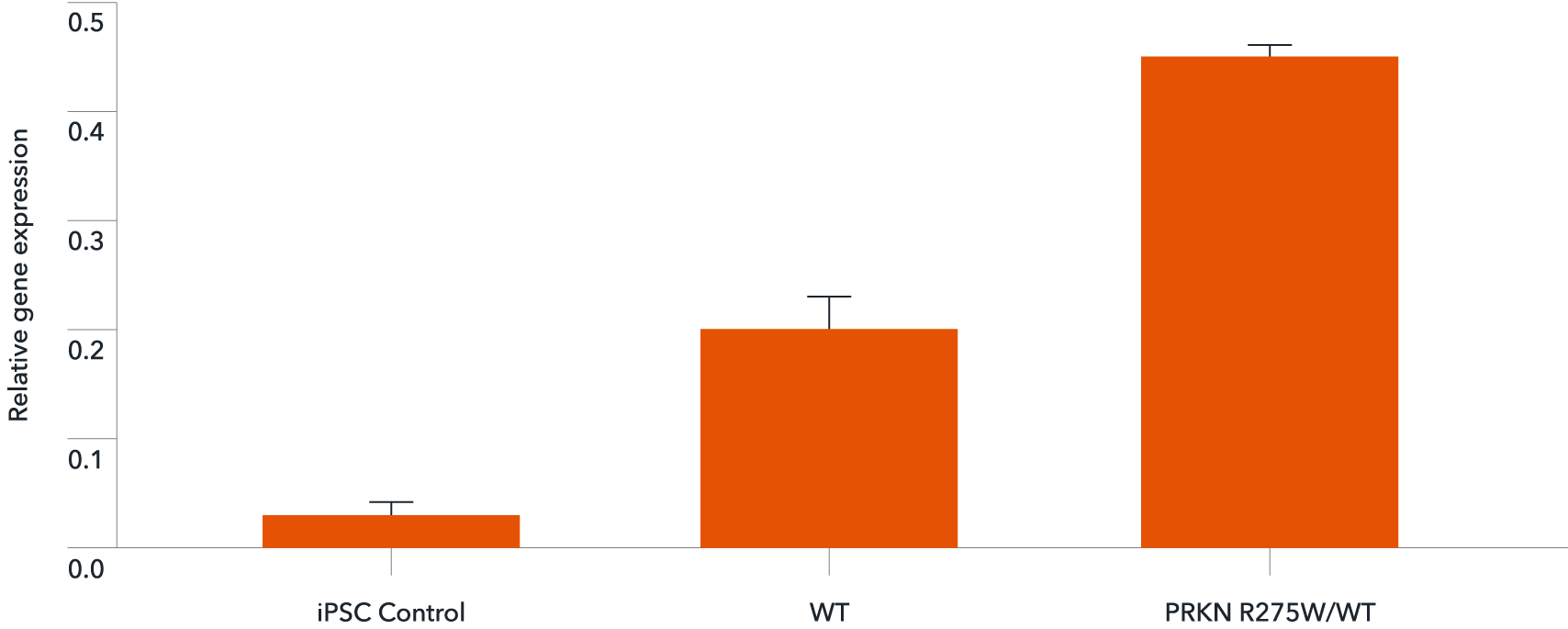
Disease-related PRKN is expressed in ioGlutamatergic Neurons PRKN R275W/WT following deterministic programming
RT-qPCR analysis demonstrates expression of the PRKN gene in both wild type ioGlutamatergic Neurons (WT) and ioGlutamatergic Neurons PRKN R275W/WT at day 11 post revival. Data normalised to HMBS, n=2 replicates.

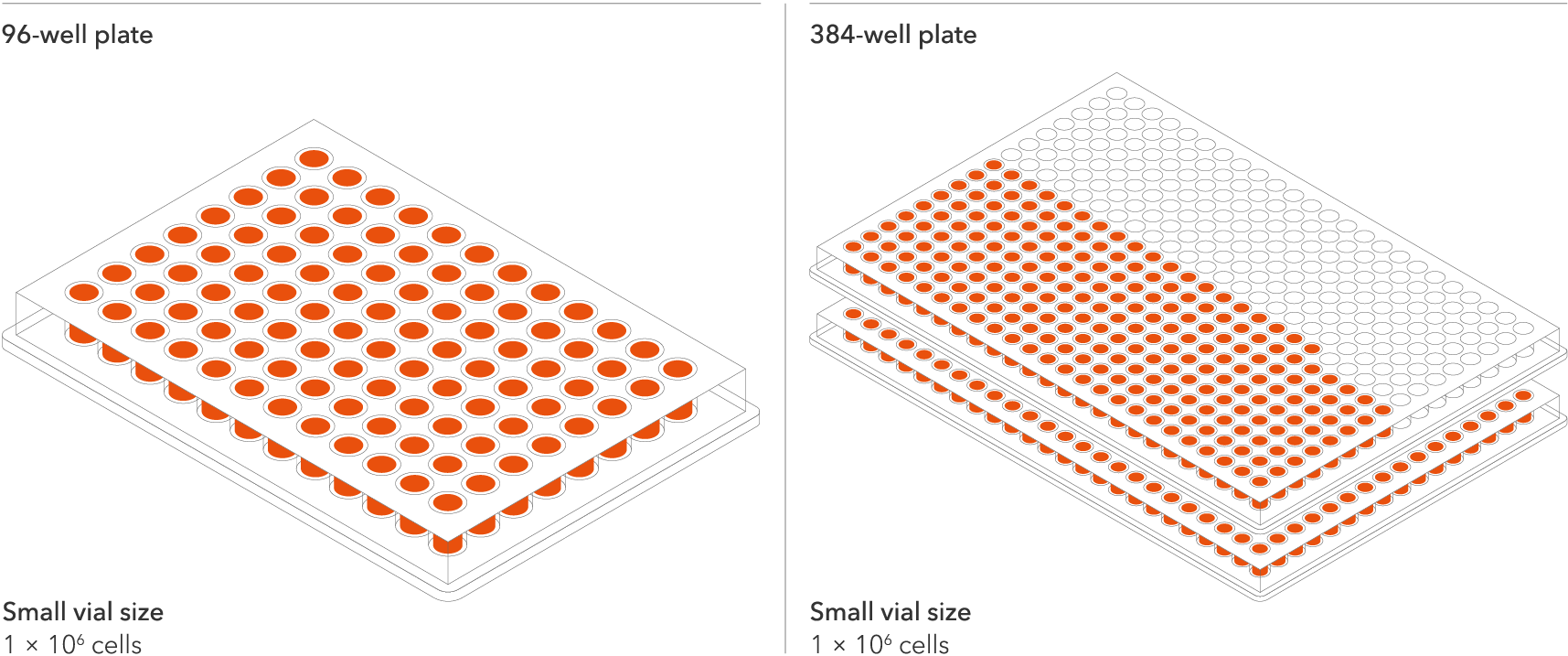
Industry leading seeding density
The recommended minimum seeding density is 30,000 cells/cm2, compared to up to 250,000 cells/cm2 for other similar products on the market. One small vial can plate a minimum of 0.7 x 24-well plate, 1 x 96-well plate, or 1.5 x 384-well plates. This means every vial goes further, enabling more experimental conditions and more repeats, resulting in more confidence in the data.
Vial limit exceeded
A maximum number of 20 vials applies. If you would like to order more than 20 vials, please contact us at orders@bit.bio.




Hoescht(blue)TUBB3(blue)_day4.png?width=604&name=bit.bio_ioGlutamatergic%20Neurons_60xMAP2(red)Hoescht(blue)TUBB3(blue)_day4.png)


.png?width=604&name=a.HTT50CAGWT__TUBB3(G).png)





.png?width=604&name=Tech%20Nets%20online%20symposium%20header%20(1).png)






-1.png?width=604&name=CRL%20video%20%231%20card%20for%20webpage%20(thinner%20gradient%20line)-1.png)


Hoescht(blue)_day12v2.png?width=604&name=bit.bio_ioGlutamatergic%20Neurons_20xMAP2(red)Hoescht(blue)_day12v2.png)
Hoescht(blue)TUBB3(blue)_day4.jpg?width=604&name=bit.bio_ioGlutamatergic%20Neurons_60xMAP2(red)Hoescht(blue)TUBB3(blue)_day4.jpg)

.png?width=1860&height=1260&name=bit.bio_3x2_ioGlutamatergic%20Neurons_MAP2_Hoescht_x20_hi.res%20(1).png)